Chinese Power Equipment Industry Overview
Industry Background and Key Drivers
In recent years, the global energy transition and the rapid growth of AI computing power have created new opportunities for the power equipment industry. The energy revolution is driving investment in renewable energy installations and grid infrastructure, while AI data centers are generating exponential growth in electricity demand. This not only increases total power consumption but also pushes the evolution of power supply architectures toward higher efficiency and higher integration.
Data centers now operate at much higher power densities, placing unprecedented demands on the efficiency and reliability of power distribution equipment. Traditional UPS solutions are gradually giving way to higher-efficiency alternatives such as High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) and Solid-State Transformers (SST). According to Guosen Securities, the global data center IT load is expected to grow at a CAGR of nearly 48% from 2024–2026. By 2026, the market size for transformers, switchgear, UPS, and HVDC supporting equipment is projected to reach CNY 7.6B, 30.4B, 30.4B, and 4.6B respectively, indicating a huge market potential for power equipment.
Overall, growth in renewable generation, grid upgrades, and AI data center construction together drive a high-growth environment for power equipment, offering significant opportunities for industry expansion.
Generation Side
On the generation side, wind and solar power dominate, with long-term prospects for controllable nuclear fusion, though this is a concept at least five years out, similar to quantum computing. While China has world-leading nuclear technology, due to technological secrecy and diverse energy options, nuclear is not the only choice for computing centers. In contrast, the U.S. largely relies on nuclear for stable baseload computing power. China holds a clear advantage in power generation equipment, but severe commoditization and price competition reduce margins, making it a less attractive business. Recent reversals in wind turbine margins are worth watching.
Grid Side
China also leads globally in ultra-high voltage (UHV) technology, which is considered state-level confidential technology and is primarily dominated by state-owned enterprises. Their performance mainly depends on national UHV line projects, with limited overseas revenue. However, several high-quality grid equipment and components companies are expanding rapidly overseas, including:
Shenma Electric (603530.SH): A domestic leader in composite insulators and related products, with over 20 years of experience in the high-voltage composite insulation market. Its products are widely used in transmission lines and substations, with market share exceeding 70% in UHV and EHV substation composite insulators. As UHV projects accelerate, demand for composite insulators grows, positioning Shenma Electric to benefit. The company maintains close partnerships with global power players such as State Grid, Southern Power Grid, GE, ABB, and Siemens, and continues to expand its product line. High-end market positioning and advanced technology also give Shenma Electric advantages in exports and high-margin business.
Siyuan Electric (002028.SZ): A domestic leader in main-grid transmission and distribution equipment, focusing on high-voltage switchgear, transformers, circuit breakers, and energy storage systems. Recognized as a “main-grid platform leader,” Siyuan has delivered stable financial growth: 2024 revenue CNY 15.46B (+24.1%), net profit CNY 2.05B (+31.4%); H1 2025 revenue CNY 8.496B (+37.8%). Siyuan has actively expanded overseas, with 2024 international revenue of CNY 3.122B (+44.7%) and nearly 89% growth in H1 2025. The company has projects and offices in the UK, Italy, Saudi Arabia, and a US subsidiary as a strategic hub. Siyuan’s product offerings are also evolving toward intelligent and higher-voltage solutions, such as networked SVGs and high-voltage energy storage systems, to support renewable penetration.
Load Side: AI Data Centers
From an investment perspective, the focus should be on the electricity-demand side (AI data centers), with stock selection priorities:
Leaders in data center distribution and HVDC/SST technologies: Their clients are cloud providers (BAT, third-party data centers), representing a TO B business closely linked to AI CapEx. Compared with grid or generation projects (TO G, state budget-driven), TO B business grows faster and offers margin expansion potential.
Internationally competitive exporters: Overseas power equipment shortages and high local costs provide pricing leverage. Companies with high overseas revenue and local facilities, particularly tied to Nvidia or other ASIC vendors, are positioned for significant upside.
Technology leadership: Companies with strong leadership in niche segments reduce commoditization risk and can maintain higher margins. R&D capabilities and alignment with evolving technology roadmaps are critical.
Evolution of Power Supply Architectures: From UPS to HVDC and SST
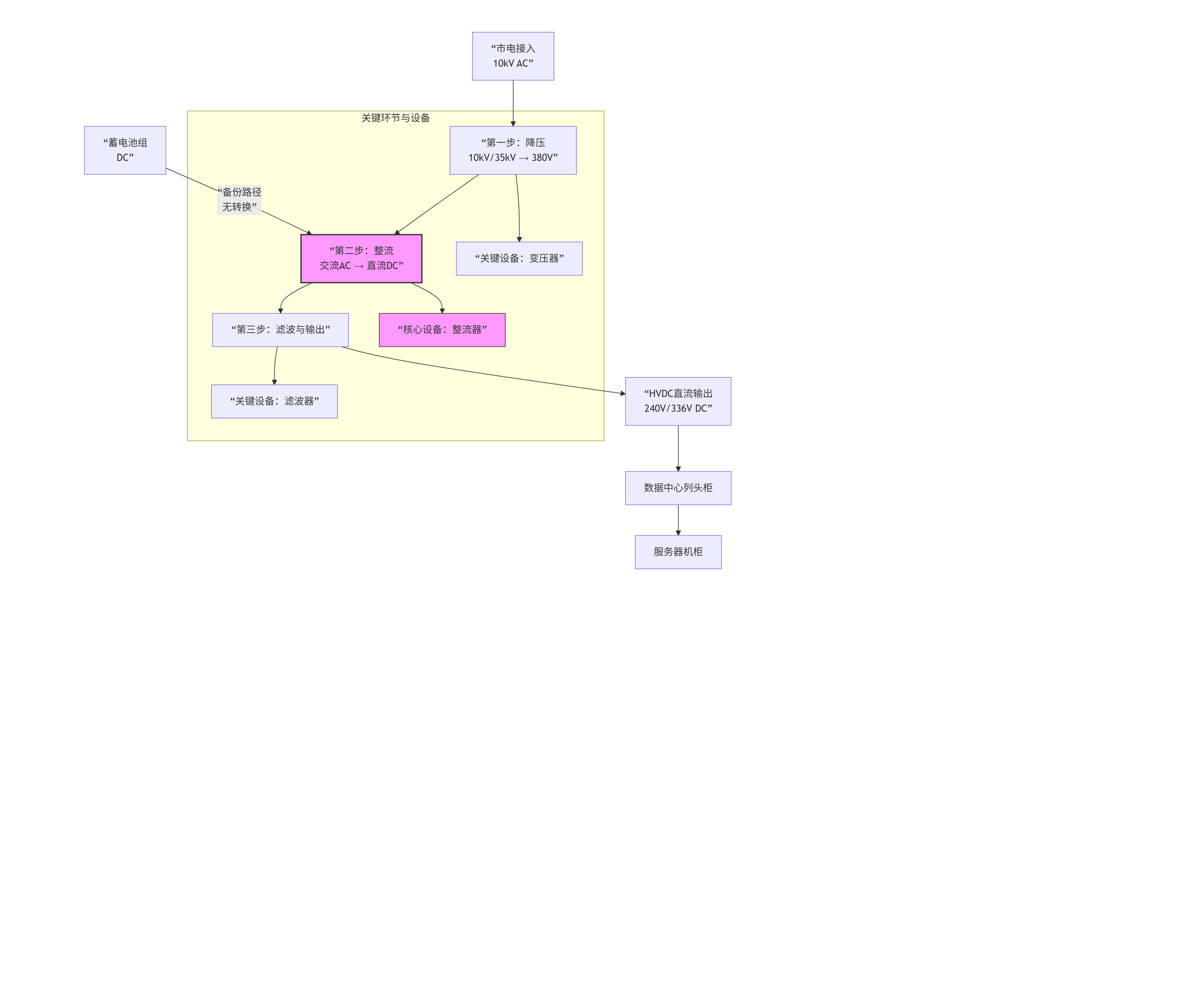
Traditional UPS Architecture
Typical path:
Mains AC → Power Transformer → UPS → Server
This architecture worked when computing loads were moderate. However, with AI servers reaching 5–10kW per unit, traditional UPS systems face bottlenecks:
Long conversion chain, low efficiency: Multiple AC/DC/AC conversions limit overall efficiency to ~93%, with significant energy losses. Even a 1% efficiency gain can save millions of kWh per year for large data centers, translating into higher effective compute capacity.
Large footprint, complex maintenance: UPS units are bulky, occupy valuable space, and maintenance downtime can lead to substantial economic loss.
HVDC Advantages
HVDC architectures use ±240V to ±800V high-voltage DC bus systems for direct server supply:
Fewer conversion stages: Eliminates UPS and some inversion steps, raising efficiency to 96–97%.
Simpler, more reliable: Fewer failure points, higher MTBF.
Smaller footprint: Saves over 30% of data center space.
Better suited for AI servers: GPUs prefer stable DC; HVDC responds better to dynamic loads.
Global cloud providers (AWS, Google, Tencent, Alibaba) are upgrading from 240/336V to ±400V or ±800V HVDC, making it a standard for AI data centers.
Next-Generation Technology: Solid-State Transformers (SST)
SSTs are the next step above HVDC. They use power electronics and high-frequency transformers to convert 10kV AC directly to high-voltage DC (±800V), eliminating traditional power-frequency transformers and rectifiers.
Advantages:
Efficiency: Increases full-chain efficiency by ~3%, approaching 99%.
Compact & modular: 60% smaller footprint, 75% shorter installation cycle.
Renewable-friendly: Directly compatible with PV and storage, flexible AC/DC conversion.
Short-term, overseas markets (North America, Europe) may still rely on traditional HVDC due to cost and reliability verification.
Core Equipment in HVDC Systems
Transformers: Change voltage levels at the front end of HVDC systems.
Rectifiers: Convert AC to DC, central to HVDC value.
Filters: Purify current, essential for power quality.
Key companies:
Transformers:
Jinpan Technology: Technological leader; SST prototypes supplied to Nvidia, binding with global compute giants.
Eaton (ETN, US): High-end market leader in energy router architectures, North America gross margins 50–55%.
Rectifiers (HVDC core):
Delta Electronics: Provides end-to-end HVDC solutions from grid to chip; samples sent to leading cloud providers.
Zhongheng Electric: 28% domestic HVDC market share; deeply integrated with Alibaba, Tencent; covers 80%+ of domestic compute nodes.
Vertiv (US): Global DC infrastructure leader; rectifiers achieve 98% efficiency.
Filters / power semiconductors:
Infineon and STMicroelectronics: Global leaders in power semiconductors, critical for 800V HVDC adoption and energy quality control.
SST Technology Evolution and Industry Impact
SST adoption affects both traditional transformer and rectifier/inverter companies.
Traditional dry-type transformer manufacturers (e.g., Jinpan) face partial replacement risk.
SST relies on AC-DC converters and high-frequency isolation transformers, meaning companies in high-frequency transformers and power electronics will benefit.
In early stages of 800V/±400V HVDC upgrades, traditional transformers still dominate—favoring transformer-focused companies. Long-term, SST and higher-integration solutions will grow rapidly, benefiting firms with power electronics expertise.
Roles of key players:
Siyuan Electric: “System integrator,” assembling complex and intelligent power modules from components.
Shenma Electric: Upstream specialist in materials and components, providing safe and cost-effective “skeleton” for the system, including SST.
Featured Chinese A-share companies:
$Jinpan Technology (SH688676)$
$Zhongheng Electric (SZ002364)$